Medical testing kits must maintain sterility, internal accuracy and contamination-free performance. The housings, sample chambers, fluid channels and diagnostic enclosures must be sealed with extreme precision to avoid leakage, cross-contamination or reagent exposure. Conventional joining methods such as adhesives pose chemical risks, while mechanical fastening can introduce particulates.
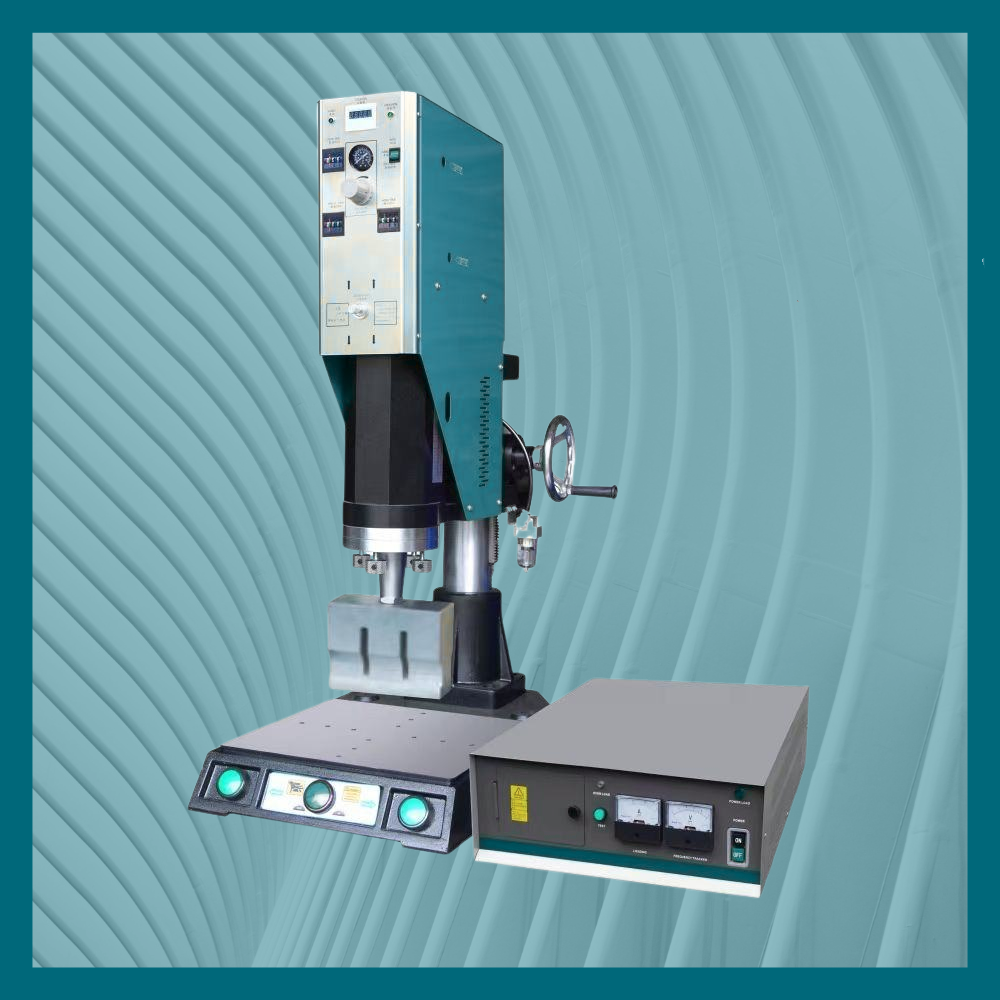
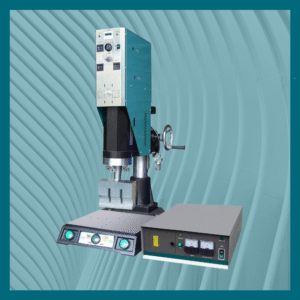
The altrAsonix Ultrasonic Plastic Welding Machine for Medical Testing Kit fuses thermoplastic components using ultrasonic vibration, creating a clean, solid, airtight weld without adhesives or solvents. This makes the process ideal for rapid-testing kits, immunoassay cartridges, microfluidic devices and point-of-care diagnostic units.
The following guide explains the plastic science, weld behavior and joint design principles that help manufacturers select the correct welding parameters for medical diagnostic kit production.
Plastic Welding Guide for Diagnostic Testing Kits
Which Plastics Can Be Welded?
Diagnostic testing kits commonly use ABS, PP, PC, PS and PMMA because these materials offer transparency, chemical stability and controlled melt behavior. All are thermoplastics, making them suitable for ultrasonic welding.
Elastomers and thermosets cannot be welded due to their chemical characteristics under heat.
Common Weldable Plastics and Their Behavior
ABS – Excellent for diagnostic housings, rigid and consistent
PP – Ideal for disposable test components needing chemical resistance
PC – Transparent parts that require toughness
PS – Common in microfluidic cartridges
PMMA – Clear but brittle; weld carefully
PVC – Selective use in diagnostic devices
Rapid test kits typically use ABS or PS, while microfluidic chambers often incorporate PC or PMMA.
Factors Influencing Weld Strength
Melting Temperature
Higher melting plastics such as PC require increased amplitude.
Melt Flow Characteristics
Improved melt flow ensures stronger and more homogeneous weld lines.
Elastic Modulus
Rigid materials transfer ultrasonic energy more effectively.
Damping Behavior
Controls the heat formed at the interface, crucial for microfluidic channels.
Joint Design for Testing Kit Components
Basic Flat Joint
Used for flat diagnostic kit covers.
Step Joint
Ensures precise alignment for test-strip cassettes.
Tongue and Groove Joint
Prevents reagent leakage in microfluidic testing devices.
Mash Joint
Used for thin plastic chambers with uniform melt distribution.
Joint With Inserted Seal
Ideal when integrating membranes or reagent-soaked pads.
These joint types ensure secure closure, fluid containment and stable diagnostic performance.
Key Features
• Sterile and airtight fusion for diagnostic housings
• Supports ABS, PS, PC, PP and PMMA
• Zero adhesive contamination
• High repeatability for mass testing kit production
• Fast cycle time with uniform weld sealing
• Long-life aluminium horn for high accuracy
• Ideal for microfluidic chambers and rapid test cassettes
• Supports delicate structures without deformation
Technical Specifications
(Medical testing kits contain small to medium ABS/PS/PC components → 20 kHz / 2000W Analog recommended)
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Model | UPM-20K-2000W-ANALOG |
| Frequency | 20 kHz |
| Power Output | 2000W |
| Welding Mode | Time / Manual |
| Rectifier Type | Analog |
| Input Voltage | AC 220V |
| Operation Type | Manual |
| Weight | Approx. 90 kg |
| Used For | Small/medium ABS/PS/PC diagnostic kit housings |
Material Compatibility
| Material | Compatible | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| ABS | Yes | Perfect for diagnostic cassettes |
| PP | Yes | Good for disposable components |
| PC | Yes | High strength and transparency |
| PS | Yes | Widely used in rapid test kits |
| PMMA | Partial | Brittle in thin channels |
| PVC | Limited | Special process needed |
| PA | No | Not weldable |
| POM | No | Not weldable |
Detailed Product Applications
The altrAsonix Ultrasonic Plastic Welding Machine for Medical Testing Kit is widely used in manufacturing of:
• Rapid antigen test housings
• Sample collection chambers
• Diagnostic cassette plastic bodies
• Microfluidic channel housings
• PCR test kit enclosures
• Immunoassay cartridge bodies
• Fluid reservoir covers
• Chemical reaction chambers
Each application requires precision sealing to ensure accurate testing performance and contamination-free structure.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.